Imf Bailout Asian Financial Crisis
asian crisis financialThe crisis hlt the most rapidly growing economies in the world and prompted the largest financial bailouts in history. Sachs believes that IMF dictated austerity measures in exchange for emergency lending was not necessary.
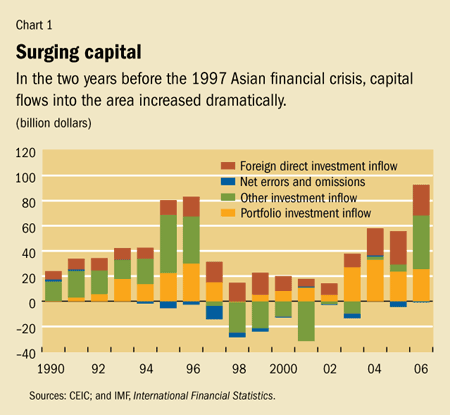 Finance Development June 2008 Point Of View Asia A Perspective On The Subprime Crisis
Finance Development June 2008 Point Of View Asia A Perspective On The Subprime Crisis
The Asian financial crisis that was triggered in July 1997 was a shocker.
Imf bailout asian financial crisis. The bailout had conditions that forced Korea to go through restructuring policies and programs such as new labor market policies that allowed more flexibility in terminating employees. In Asia hundreds of thousands of people have lost their jobs as insolvent factories close. Since the Asian financial crisis was caused by the poor economic and financial policies of East Asian governments no amount of IMF and US.
From the perspective of a member of the Executive Board of the IMF as Asian problems were building the IMF overlooked weaknesses in bank and corporate balance sheets in much of Asia. The International Monetary Fund created a series of bailouts rescue packages for the most-affected economies to enable them to avoid default tying the packages to currency banking and financial system reforms. His basic premise is that during the East Asian Economic Crisis the IMF failed in its job of being a lender of last resort thus exacerbating the crisis and making the situation much worse than it should have been for the countries involved.
IMFs Role in the Asian Financial Crisis The International Monetary Fund IMF is an international organization that promotes global monetary cooperation and international trades reduces poverty and supports financial stability. On August 20 1997 the IMF announced an assistance package of 4 billion for Thailand. The Asian crisis first emerged in Thailand in 1997 as the baht came under a series of increasingly serious speculative attacks and markets lost confidence in the economy.
IMF agreed to provide Indonesia with a 40-billion-dollar bailout package and in return had to close down 16 insolvent financial institutions and a wide range of structural reforms South Korea on the other received the biggest ever bailout package of 57 billion amid much domestic criticism. Treasury is the largest financial rescue plan in history. On August 20 1997 the IMFs Executive Board approved financial support for Thailand of up to SDR 29 billion or about US4 billion over a 34-month period.
South Korea signed the agreement with the IMF to address their deficients due to the 1997 Asian financial crisis. The East Asian financial crisis is remarkable in several ways. This paper analyzes the origins implications and solutions for the Asian financial crisis.
Thus began the IMFs involvement in the Asian financial crisis. The ensuing debate should be a healthy part of the process by which the institution is held accountable to its member countries and governments. Due to IMFs involvement in the financial crisis the term IMF became synonymous with the Asian Financial Crisis itself.
The late 1990s Asian financial crisis was caused in large part by South Korea Thailand the Philippines Malaysia and Indonesias heavy reliance on short-term foreign loans and openness to hot. Financial aid will compel them to make the fundamental. Over the 20 years since the nominal end of the bad times the legacy of the crisis is a reorientation of the countrys systems of employment and a growing increase in inequality.
What was at the time perceived to be a. The Fund made loan arrangements to enable countries to meet foreign debt payments largely to private banks in these cases on the condition that the recipient. Total job losses could be in the millions.
The IMF involvement in the Thai crisis resulted in the strengthening of expectations of further IMF bailouts. The structural provisions included. The IMF generated several bailout packages for the most affected countries during the financial crisis.
It is the least anticipated financial crisis in years. Key Points The 120 billion bailout for four troubled Asian economies crafted bythe IMF and the US. While he acknowledges some IMF successes in firefighting financial crises in Mexico and East Asian countries in the mid-1990s he criticizes many of the funds interventions in severely.
The IMF was unaware of the extraordinary leverage of Korean companies which in some cases reached a ratio of 6001 debt to equity. As the crisis spread the IMFs commitments. The IMF treated the Asian financial crisis like other situations where countries could not meet their balance of payment obligations.
It is the sharpest financial crisis to hit the developing world since the 1982 debt crisis. Consequently the IMF created a strong contagion effect whereby having rescued the Thai creditors it greatly increased the expectation that the creditors of other countries would also be rescued. The Asian crisis and the Administrations request to Congress for IMF funding have focused unprecedented attention on the Fund.
The 1997-98 Asian Financial Crisis known invariably in South Korea as the IMF Crisis was such an event. Even two years after it ended anxiety still loomed over global financial markets.